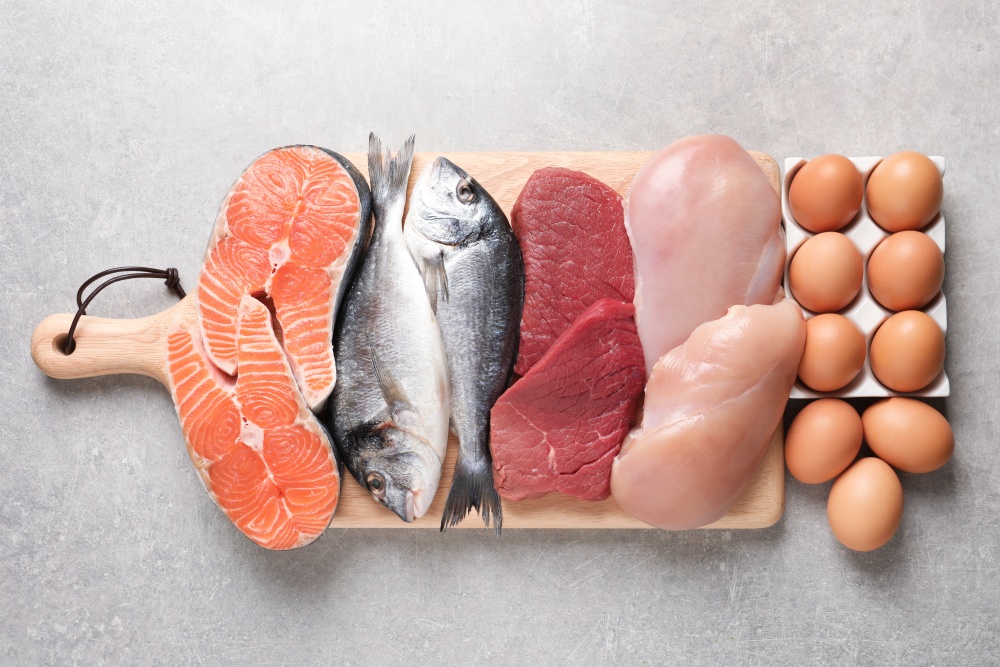
Protein, often referred to as the “building blocks of life” is arguably the most critical macronutrient for brain health and repair and disease prevention as we age. One of three macronutrients found in food the body is primarily composed of protein (second only to water).
Proteins are essential for the growth, repair, and maintenance of tissues in the body (muscles and bone integrity), and they also play a role in many other bodily functions, such as enzyme production, hormone regulation, and immune system function.
All of that said, in this article, you will learn the critical role of protein in the body, the different types and implications on brain health, and how to ensure you are getting adequate protein in your diet to maintain brain health and prevent disability as you age.
Protein Metabolism
The body has a complex system for regulating the production and breakdown of proteins. This process is called protein metabolism.
Protein Catabolism
Protein catabolism is the process of breaking down the protein in food into amino acids that are then absorbed into the bloods stream.
Protein Anabolism
Protein anabolism is the processed of taking the amino acids and converting them into functional proteins.
Amino Acids
Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins. There are 20 different amino acids that the body needs to function properly, and they can be divided into two categories: essential and non-essential. Essential amino acids cannot be produced by the body and must be obtained through the diet, while non-essential amino acids can be produced by the body.
There are 9 amino acids that cannot be produced by the body and must be consumed through food. These include
- Valine
- Isoleucine
- Leucine
- Methionine
- Phenylalanine
- Tryptophan
- Threonine
- Histidine
- Lysine
What is the function of amino acids in the body?
- Tissue growth and repair
- Enzymes used for bodily functions (digestion, energy production, blood clotting, and muscle contraction)
- Act as hormones: chemical messengers that allow cells to communicate with one another
Protein Deficiency
It is important to note that if one essential amino acid is not available, protein synthesis can’t occur. With that said, protein deficiency (hypoproteinemia) has been linked to:
- Muscle loss
- Slowed growth
- Weakened immune system
- Weakened lungs and heart
What is a complete protein?
Foods that contain all of the essential amino acids are called complete proteins. These foods include:
- Beef
- Poultry
- Fish
- Eggs
- Dairy
- Soy
- Quinoa
- Buckwheat
Do amino acid supplements work?
There is little evidence that amino acid supplements are effective in protein synthesis in the body
Can you eat too much protein?
Consuming too much protein can also have negative effects on the body. Excess protein is converted into fat and stored in the body, which can lead to weight gain. It can also put a strain on the kidneys, which are responsible for filtering out waste products from the body.
Plant versus Animal Protein
Plant proteins and animal proteins differ in several ways, including their amino acid profiles, digestibility, and nutrient content. It is important to note that plant proteins do not contain all 9 essential amino acids.
Amino acid profiles
Animal proteins, such as those found in meat, eggs, and dairy products, are considered “complete” proteins because they contain all of the essential amino acids that the body needs. Plant proteins, on the other hand, are often considered “incomplete” because they may be lacking in one or more essential amino acids.
Digestibility
Animal proteins are generally more easily digested and absorbed by the body than plant proteins. This is because animal proteins are more similar in structure to human proteins, making them easier for the body to break down and use. Plant proteins, on the other hand, may contain compounds that interfere with digestion and absorption, such as phytates and fiber.
Nutrient content
Animal proteins are often higher in certain nutrients, such as vitamin B12, iron, and zinc, than plant proteins. However, plant proteins are often higher in other nutrients, such as fiber, antioxidants, and phytochemicals.
With all that said, plant-based diets require a deep understanding of how to combine plant proteins to ensure the body is getting all 9 essential amino acids to make it a complete protein. For example, beans are NOT a complete protein and must be combined with rice.
Articles you may be interested in:
Good, Evil,….. and Justice
I believe the hardest thing a human can do is to radically accept unfavorable circumstances. Maybe it's just me, but there is something deep inside every human that craves justice. Not just for ourselves, but for the world. Webster tells me that the definition of...
Exploring the Connection Between Sleep and Weight Loss
An estimated 50 to 70 million people in the U.S. are battling chronic insomnia and sleep disorders. These seemingly harmless conditions brought on by stress, changes in sleep schedules or lifestyles, and medications can be quite disruptive. Over time, it can lead to...
Soothing Stress With Sound Therapy
Seventy-six percent of U.S. adults reported that they experienced at least one symptom of stress in the last month such as headaches, fatigue, nervousness, anxiety, depression, and sadness. It’s easy to see why. Americans are among the most stressed out people in the...
12 Clever Ways To Healthy Eating on a Budget
Inflation and supply-chain disruptions have caused food prices to shoot up more quickly than in previous decades, making every trip to the grocery a costly and tricky affair. Despite the fact that food has become more expensive than ever, the federal minimum wage...
Volunteering: How Helping Others May Impact Overall Health
Volunteering is a pro-social behavior. It’s dedicating your time, attention, and resources toward helping people who are facing hardships in your community with no expectation of any reward or compensation. But there is something in it for you after all. Volunteering...
The Unseen Connection: Oral Health’s Surprising Impact on Heart Health
Did you know that the benefits of maintaining oral health go beyond your mouth? Oral health—the health of your teeth, gums, alveolar bone, etc.—plays a more significant role than you think. Sure, it keeps your gums and teeth clean and healthy. It also helps with basic...
Whispers to Wonders: Unraveling the allure of ASMR
You may have come across the term “ASMR” at least once, particularly if you’ve been on certain corners of social media. Be it TikTok, Instagram, or even YouTube, ASMR videos have been all the rage. Tapping, scratching, whispering, chewing—ASMR (autonomous sensory...
Mind Your Memory: Naturally Nurturing Your Cognitive Strength
Your memory is an intricate tapestry woven with knowledge, experience, and personal history, which forms the cornerstone of human cognition. However, as is the case with any tapestry, your memory will start to wear out with time, and your cognitive health may decline...
Silent Storms: The Atypical Form of Depression You Need to Know More About
Approximately 280 million people suffer from depression on a global scale. The figure is harrowing but doesn’t give you the complete picture because depression isn’t always visible. Sometimes, people experience symptoms related to it but can’t pinpoint what they’re...
Understanding The Link Between L-Theanine and Stress
Introduction Today, stress is one of the leading causes of physical challenges. Yes, what used to be a feeling of tension or a state of mind when faced with a difficult situation can impact you physically and even how you react and handle things emotionally and...